1917
A revised edition of the 1913 uniform regulations was published in January 1917, and included the shoulder marks that had been temporarily eliminated in 1913.1 The uniforms prescribed were those worn when the United States entered the First World War.
| Cap Badge |  |
||||||
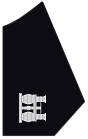
| Frock Coat Collar (Right Side) |
 |
 |
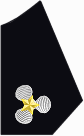 |
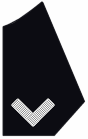 |
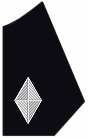 |
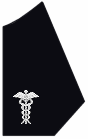 |
 |
| Blue Service Coat Collar (Right Side) |
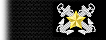 |
 |
 |
 |
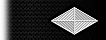 |
 |
 |
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
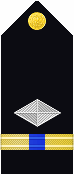 |
 |
 |
| Sleeve |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Chief Boatswain | Chief Gunner | Chief Machinist | Chief Carpenter | Chief Sailmaker | Chief Pharmacist | Chief Pay Clerk | |
| Cap Badge |  |
|||||||||
| Frock Coat Collar (Right Side) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
||
| Blue Service Coat Collar (Right Side) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
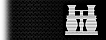 20 years in rank 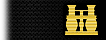 under 20 years |
||
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
||
| Sleeve | 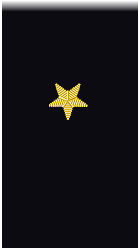 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Boatswain | Gunner | Machinist | Carpenter | Sailmaker | Pharmacist | Pay Clerk | Mate | |||
1918
In August 1918 Secretary of the Navy Josephus Daniels ordered that distinctions between line and staff officers be minimized. In November 1918 a uniform regulations change was issued to implement the directive.2 Commissioned warrant and warrant officers of the staff specialties were ordered to wear their corps device on the cuff, in the same position as the line star. These sleeve devices would be in gold for both grades, and sized to fit within a one-inch circle.
| Cap Badge |  |
||||||
| Frock Coat Collar (Right Side) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Blue Service Coat Collar (Right Side) |
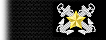 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Sleeve |  |
 |
 |
 |
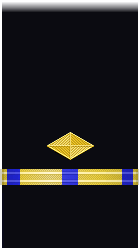 |
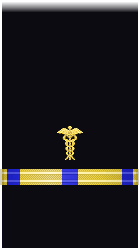 |
 |
| Chief Boatswain | Chief Gunner | Chief Machinist | Chief Carpenter | Chief Sailmaker | Chief Pharmacist | Chief Pay Clerk | |
| Cap Badge |  |
|||||||||
| Frock Coat Collar (Right Side) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
||
| Blue Service Coat Collar (Right Side) |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 20 years in rank  under 20 years |
||
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
||
| Sleeve |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
||
| Boatswain | Gunner | Machinist | Carpenter | Sailmaker | Pharmacist | Pay Clerk | Mate | |||
1919
In March 1919 the Navy Department announced that the officers' service dress blue coat would be changed from the single breasted style with standing collar and black braid trim to double-breasted with a rolling collar and lapels.3 The collar devices would be eliminated, so corps devices above the rank stripes would be the sole indication of specialty. Regulations specifying the insignia for the new uniform were issued in November 1919.4 The United States Navy had been working closely with the Royal Navy during the war, and just as the new service dress was similar to the British pattern, so were the insignia now adopted for commissioned warrant and warrant officers. As commissioned officers, CWOs would now wear the same half-inch gold stripe as ensigns, eliminating the previous blue breaks. Warrant officers wore a gold stripe of quarter-inch width. The device for pay clerks was differentiated from commissioned supply corps insignia by removing the acorns. Mate, technically an enlisted grade, wore the corps device alone without a stripe, no longer differentiated by seniority.
| Cap Badge |  |
||||||
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
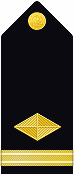 |
 |
 |
| Sleeve | 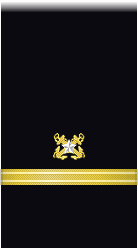 |
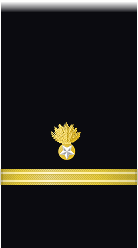 |
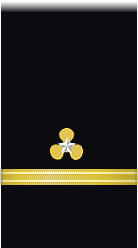 |
 |
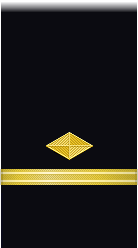 |
 |
 |
| Chief Boatswain | Chief Gunner | Chief Machinist | Chief Carpenter | Chief Sailmaker | Chief Pharmacist | Chief Pay Clerk | |
| Cap Badge |  |
|||||||
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Sleeve | 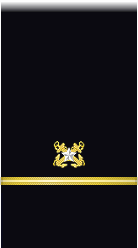 |
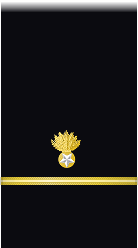 |
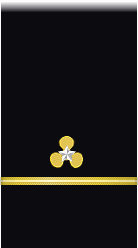 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Boatswain | Gunner | Machinist | Carpenter | Sailmaker | Pharmacist | Pay Clerk | Mate | |
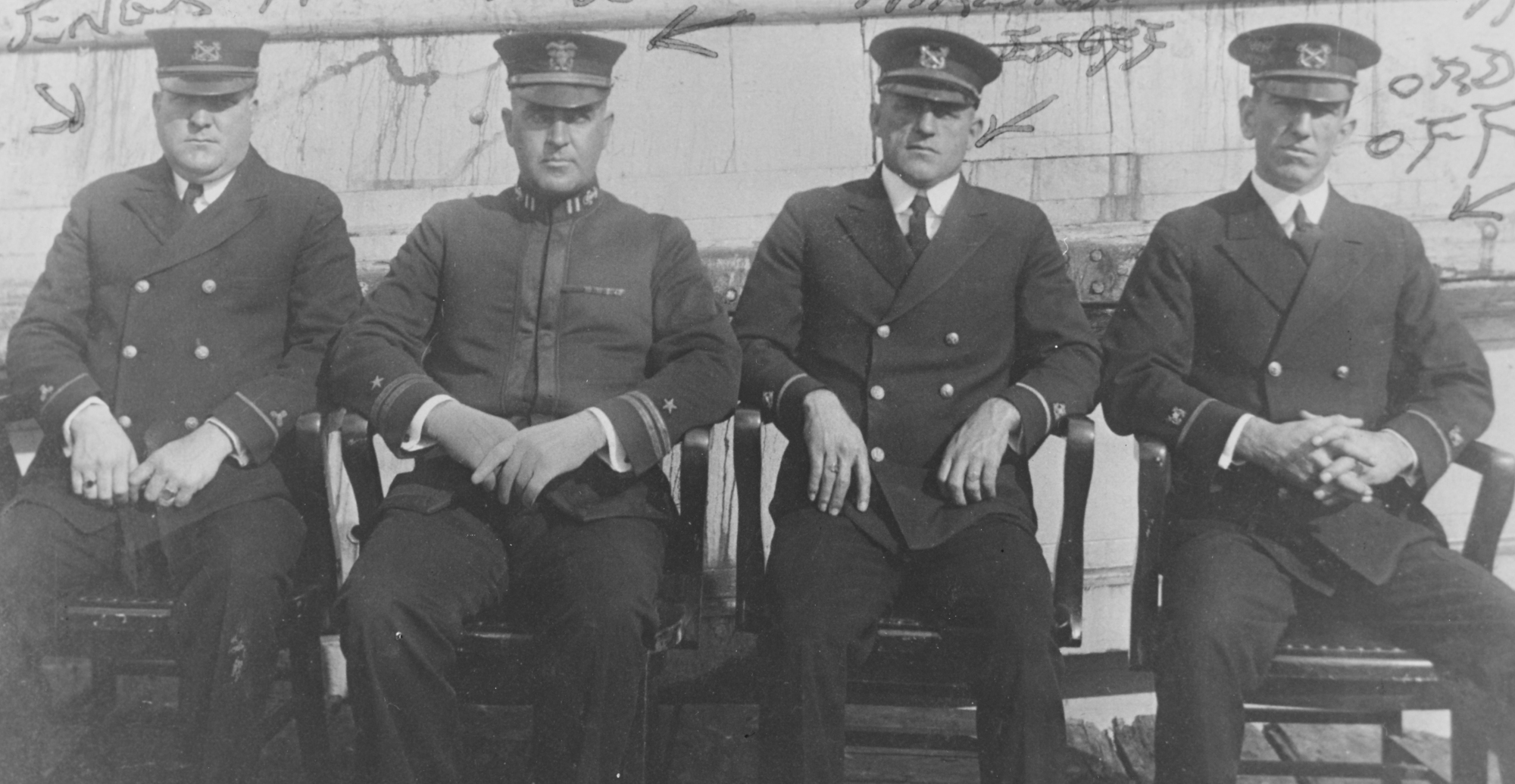 |
| Officers of the USS Conestoga, 1921. The warrant officers are wearing gold stripes without blue breaks as used between 1919 and 1922. The lieutenant is wearing the pre-1919 blue service dress. Photo from the Naval History and Heritage Command. |
1922
New uniform regulations were issued in 1922, incorporating the changes made during and after World War I.5 For CWOs and WOs, it brought a return to the blue-broken stripes of earlier years. The contrasting stars for line officers were also eliminated, leaving the corps device alone to denote line status. The space between the stripe and the end of the shoulder mark was changed from one-quarter inch to half an inch.
| Cap Badge |  |
||||||
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Sleeve |  |
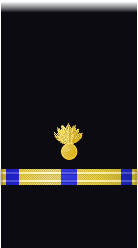 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Chief Boatswain | Chief Gunner | Chief Machinist | Chief Carpenter | Chief Sailmaker | Chief Pharmacist | Chief Pay Clerk | |
| Cap Badge |  |
|||||||
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
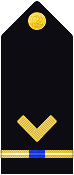 |
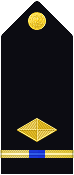 |
 |
 |
 |
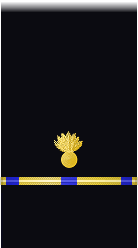
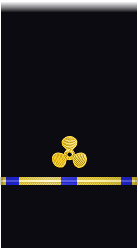
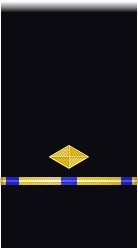
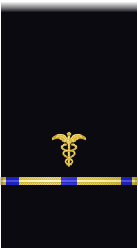
| Sleeve | 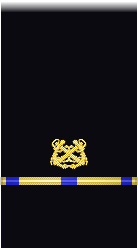 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
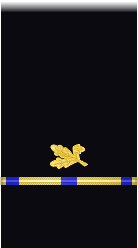 |
 |
| Boatswain | Gunner | Machinist | Carpenter | Sailmaker | Pharmacist | Pay Clerk | Mate | |
1925
The Naval Omnibus Act of 1925 created the the new warrant specialties of electrician and radio electrician. Change Number 7 to the 1922 uniform regulations authorized corps devices for the new grades, based on established petty officer specialty marks.6
| Cap Badge |  |
|
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
| Sleeve |  |
 |
| Chief Electrician | Chief Radio Electrician | |
| Cap Badge |  |
|
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
| Sleeve | 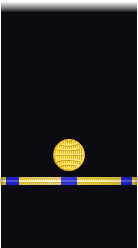 |
 |
| Electrician | Radio Electrician | |
Also authorized in 1925 were working uniforms for aviation personnel.7 The winter working uniform was forestry green wool, and the summer uniform was khaki cotton. On both uniforms, rank and corps was shown with black braid and embroidery. No breaks in the stripes were used for warrant officers.
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Chief Electrician | Carpenter | Chief Machinist | Radio Electrician |
| Aviation Working Dress (Winter) | Aviation Working Dress (Summer) | ||
1931
In March 1931 Change Number 7 to the 1922 uniform regulations authorized the khaki working uniform to be worn by submarine as well as aviation personnel, and provided for insignia to be worn on the collar of the shirt of the aviation and submarine working uniform when it was worn without a coat.8 The details of the insignia were not given, however, except that they were to be a "metal pin device." For commissioned officers it can be assumed that the same devices as used on similar Marine Corps uniforms would be worn. For warrant officers, it seems likely that metal insignia in gold and silver, similar to those used briefly in 1913, would now be used. But it was not until the 1941 uniform regulations that the details of the collar devices were specified.
1941
A major revision of the uniform regulations was in the works for 1941. In advance of its publication, orders were issued authorizing the khaki working uniform for all officers,9 and deleting the black sleeve insignia previously used on khaki in favor of shoulder marks.10 In the new uniform regulations effective May 31, the details of the collar devices were specified: Commissioned warrant devices were to be silver metal and warrant officers gold, and worn on both sides of the collar.11 Asymmetrical collar devices were worn in mirrored pairs. The collar devices were to be approximately five-eighths the size of the sleeve or shoulder mark devices, but for better visibility they are illustrated at a larger scale in the following tables.
The 1941 uniform regulations also contain the last mention of insignia for sailmakers and mates, unchanged from 1922. The last retired mate had died in 1923, the last retired chief sailmaker in 1933.
| Cap Badge |  |
|||||||
| Collar Devices | 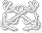 |
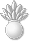 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Sleeve |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Chief Boatswain | Chief Gunner | Chief Machinist | Chief Carpenter | Chief Pharmacist | Chief Pay Clerk | Chief Electrician | Chief Radio Electrician | |
| Cap Badge |  |
|||||||
| Collar Devices |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Sleeve |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Boatswain | Gunner | Machinist | Carpenter | Pharmacist | Pay Clerk | Electrician | Radio Electrician | |
1942
In 1942 four new warrant officer classifications were approved by Congress: Chief torpedoman and torpedoman, chief ship's clerk and ship's clerk, chief aerographer and aerographer, chief photographer and photographer. In August, new devices were approved, based once again on established petty officer specialty marks.6
| Cap Badge |  |
|||
| Collar Devices |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Sleeve |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Chief Torpedoman | Chief Ship's Clerk | Chief Aerographer | Chief Photographer | |
| Cap Badge |  |
|||
| Collar Devices |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Shoulder Marks |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Sleeve |  |
 |
 |
 |
| Torpedoman | Ship's Clerk | Aerographer | Photographer | |
1943
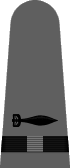
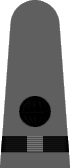
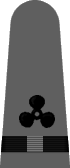
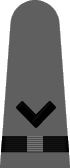
In May of 1943 it was announced that a gray working uniform would replace the khaki one,12 and in August the specifications were incorporated into the uniform regulations.13 Similar in cut to the khaki uniform, the working gray would have blue-black plastic buttons instead of gold and narrower gray shoulder marks with black braid stripes and black embroidered corps insignia. Until the gray and black accessories were widely available, the traditional shoulder marks and gold buttons were permitted. The gray uniform proved unpopular and there was so much khaki in the supply system that gray never did supplant khaki as the standard working uniform for officers and chief petty officers.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
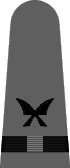 |
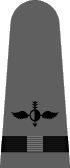 |
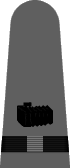 |
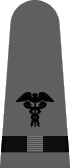 |
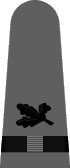 |
| Chief Boatswain | Chief Gunner | Chief Torpedoman | Chief Electrician | Chief Radio Electrician | Chief Machinist | Chief Carpenter | Chief Ship's Clerk | Chief Aerographer | Chief Photographer | Chief Pharmacist | Chief Pay Clerk |
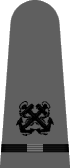 |
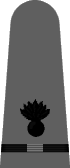 |
 |
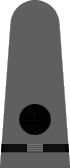 |
 |
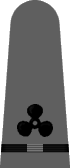 |
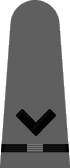 |
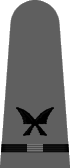 |
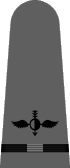 |
 |
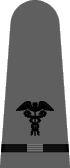 |
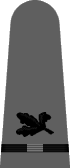 |
| Boatswain | Gunner | Torpedoman | Electrician | Radio Electrician | Machinist | Carpenter | Ship's Clerk | Aerographer | Photographer | Pharmacist | Pay Clerk |
Also authorized in 1943 were garrison caps for all officers, previously worn only by aviation personnel. Commissioned warrant officers wore a miniature cap device on the left side of the garrison cap and their silver pin corps device on the right side. Warrant officers wore gold corps devices on both sides of the garrison cap.14
With the expansion of the Navy's construction forces in 1942, warrant officers were authorized for reservists in the Civil Engineer Corps. Insignia using the commissioned Civil Engineer Corps devices were authorized,15 but the author does not have a date for the authorization.
| Cap Badge |  |
 |
| Collar Devices |  |
 |
| Shoulder Mark | 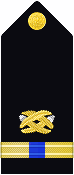 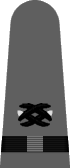 |
 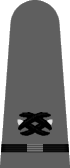 |
| Sleeve |  |
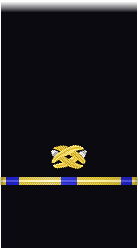 |
| Chief Carpenter, Civil Engineer Corps |
Carpenter, Civil Engineer Corps |
1944
In May 1944, the warrant officers' sleeve stripes were modified for the forestry green aviation winter working uniform. Instead of being plain black, the stripes were now to have green breaks of the same type as the blue breaks on the gold stripes.16
 |
 |
| Chief Aerographer | Photographer |
Part 3: 1947-2003 >
- 1. U.S. Navy Department, Uniform Regulations, United States Navy together with Uniform Regulations Common to Both Navy and Marine Corps, Revised to January 1917, Washington D.C., Government Printing Office, 1917.
- 2. U.S. Navy Department, "Change in Uniform Regulations, United States Navy, 1913. No. 25", November 16, 1918.
- 3. U.S. Navy Department, "Change in Uniform Regulations, United States Navy, 1913. NO. 27", March 17, 1919.
- 4. U.S. Navy Department, "Changes in Uniform Regulations, United States Navy, 1913. No. 28", November 13, 1919.
- 5. U.S. Navy Department, Uniform Regulations, United States Navy, 1922, Washington DC, Government Printing Office, 1922.
- 6. U.S. Department of the Navy, Naval History and Heritage Command, "Insignias U.S. Navy Uniform", "Insignia of Warrant Officers".
- 7. U.S. Navy Department, "Uniform Regulations Change Number 2, Uniform Regulations of 1922," October 7, 1925.
- 8. U.S. Navy Department, "Uniform Regulations Change Number 7, Uniform Regulations of 1922," March 31, 1931.
- 9.U.S. Navy Department, Bureau of Personnel Circular Letter 28-41, March 11, 1941.
- 10. U.S. Navy Department, ALNAV 32, April 5, 1941.
- 11. U.S. Navy Department, Uniform Regulations, United States Navy, 1941, Washington D.C., Government Printing Officer, 1941.
- 12. U.S. Navy Department, Bureau of Naval Personnel Information Bulletin, May 1943, p. 45.
- 13.U.S. Navy Department, Bureau of Personnel Circular Letter 153-43, August 11, 1941.
- 14.U.S. Navy Department, Bureau of Naval Personnel Information Bulletin, February 1943, p. 33.
- 15. Arthur Ageton, The Naval Officer's Guide, New York, McGraw Hill, 1944.
- 16. U.S. Navy Department, Bureau of Personnel Circular Letter 145-44, May 15, 1944.